Exploring the Vagus Nerve: A Key Player in Digestion
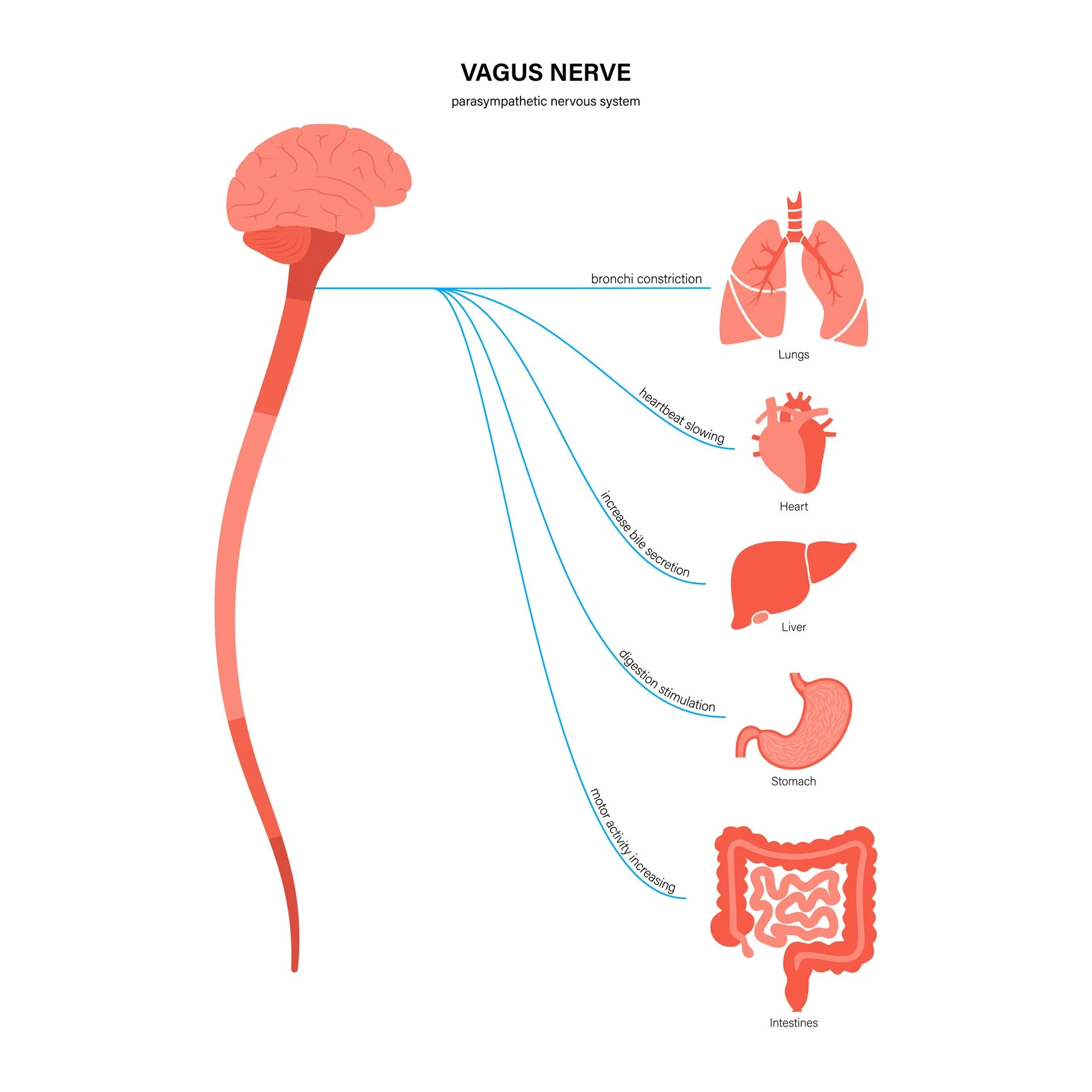
Through the processes of our bodily functions, the vagus nerve assumes a crucial role, facilitating a clear interaction between the brain and the digestive system. Known as the "wandering nerve", the 10th (and longest) cranial nerve travels from the brainstem through the neck, chest, and abdomen, connecting with vital organs, including the heart, lungs, and the digestive tract.
The Vagus Nerve and Its Role
The vagus nerve plays a pivotal role in the parasympathetic nervous system, influencing the mind-gut axis, which is a dynamic connection between the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system in the gut. This bidirectional communication not only shapes our digestion but also profoundly impacts our emotional wellbeing.
The Vagus Nerve in Action
The Vagus Nerve impacts various functions such as heart rate and blood pressure regulation, controlling the pace and depth of breathing, immune response regulation, emotional regulation and of course, digestion. For the purpose of this article we will focus mainly of its impacts on the gut.
When activated, the vagus nerve releases acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that sets the stage for digestion by stimulating the production of gastric juices and digestive enzymes. This initiation of the digestive process ensures optimal nutrient absorption and overall gut health.
The vagus nerve also engages in a constant dialogue with the gut microbiome, influencing the composition and activity of trillions of microbes residing in our digestive system. This bidirectional communication fosters a balanced microbiome, essential for efficient digestion and immunity.
Beyond digestion, the vagus nerve plays a role in regulating inflammation in the gut. This function is vital in preventing chronic inflammatory conditions such as Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD).
The Practice of Vagal Toning
A concept gaining recognition in recent years is "vagal toning", which involves practices that enhance the tone and function of the vagus nerve. Deep, diaphragmatic breathing, mindfulness techniques, and certain physical exercises including yoga and meditation contribute to vagal toning, promoting a state of relaxation that positively influences digestion and overall wellbeing.
There are also some specific Vagus Nerve Exercises that have been created and found to be very effective to switch your system into a parasympathetic state (the relaxed state also called “rest and digest”). If you look up vagus nerve exercises online, you will find lots of great videos for inspiration or alternatively, you can download this short Vagus Nerve PDF for free. :)
Understanding the connection between the vagus nerve and digestive health opens new avenues for management of conditions such as IBS and SIBO. By nurturing the vagus nerve through practices that promote relaxation, mindfulness, and vagal toning, we contribute to the balance of our gut function and microbiome. It is often a part that is missed by most people when addressing their gut issues, and I find that working on nervous system regulation is key to long-lasting healing and relief.